HTML Introduction
What is HTML?
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements are represented by tags
- HTML tags label pieces of content such as "heading", "paragraph", "table", and so on
- Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to render the content of the page
A Simple HTML Document
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
- The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines this document to be HTML5
- The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page
- The <head> element contains meta information about the document
- The <title> element specifies a title for the document
- The <body> element contains the visible page content
- The <h1> element defines a large heading
- The <p> element defines a paragraph
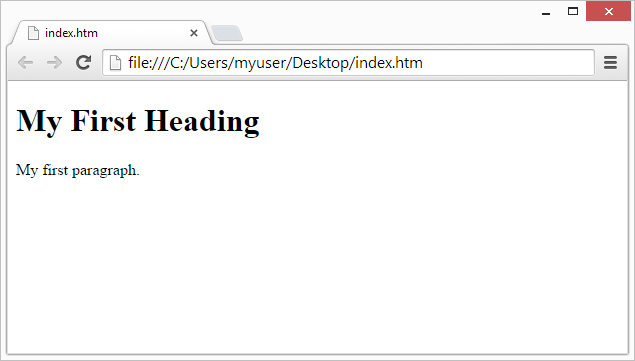
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read
HTML documents and display them.
The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine
how to display the document:
The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration represents the document type, and helps browsers to display web pages correctly.
It must only appear once, at the top of the page (before any HTML tags).
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration is not case sensitive.
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration for HTML5 is:
<!DOCTYPE html>
CSS Intoduction
What is CSS?
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen, paper, or in other media
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- External stylesheets are stored in CSS files
Why Use CSS?
CSS is used to define styles for your web pages, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes.
CSS Saves a Lot of Work!
The style definitions are normally saved in external .css files.
With an external stylesheet file, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
CSS Syntax
A CSS rule-set consists of a selector and a declaration block:
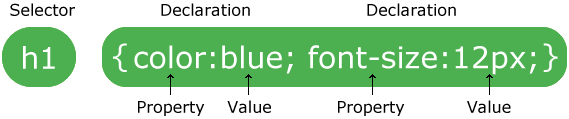
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
A CSS declaration always ends with a semicolon, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces.
Example
In this example all <p> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
The CSS id Selector
The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
The id of an element is unique within a page, so the id selector is used to select one unique element!
To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
Example
The CSS rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1":
#para1 {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
Note:An id name cannot start with a number!
The CSS class Selector
The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute.
To select elements with a specific class, write a period (.) character, followed by the class name.
Example
In this example all HTML elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
.center {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
You can also specify that only specific HTML elements should be affected by a class.
Example
In this example only <p> elements with class="center" will be center-aligned:
p.center {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
The CSS Universal Selector
The universal selector (*) selects all HTML elements on the page.
Example
The CSS rule below will affect every HTML element on the page:
* {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}